En el mundo de la fabricación y la logística, “máquinas empacadoras” y “máquinas empacadoras” se usan a menudo como si significaran lo mismo. Pero no lo hacen. Si bien ambos pertenecen a la misma familia de automatización, Sirven para diferentes propósitos en su línea de producción.. Comprender esta diferencia le ayuda a mejorar la eficiencia, controlar costos, y mantener la calidad del producto.
Echemos un vistazo más de cerca a lo que hacen., en qué se diferencian, y cómo elegir el equipo adecuado para su negocio.
¿Qué son las máquinas empacadoras y envasadoras??

Una máquina envasadora se centra en la contención y protección del producto.. Garantiza que cada artículo se llene de forma segura., sellado, o en caja antes del envío o almacenamiento. En muchas fábricas, Las máquinas empacadoras se encargan de operaciones como el pesaje., harpillera, caza de focas, o etiquetado. Por ejemplo, una máquina llenadora de polvo mide y llena cada paquete con un peso preciso. Una máquina selladora de cajas de cartón cierra las cajas firmemente para evitar contaminación o fugas.. El objetivo es garantizar que los productos sigan siendo seguros., estable, y listo para el manejo logístico.
Una máquina envasadora se ocupa de la capa exterior que define cómo se presenta un producto al mercado.. Le da al producto su aspecto comercial final y a menudo integra la impresión., envoltura de películas, o formación de cajas de cartón. En las industrias de alimentos y bienes de consumo., máquinas de embalaje imprimen códigos de barras, aplicar gráficos de marca, y envolver artículos en materiales listos para la venta al por menor. El objetivo no es sólo mantener la calidad sino también cumplir con las expectativas de marketing., etiquetado, y estándares de cumplimiento.
Diferencias clave entre máquinas empacadoras y empacadoras

1. Función y rol principal
Máquinas de embalaje
• Centrado en agrupar, caza de focas, y preparar productos terminados para su envío o almacenamiento.. Organizan los productos para que sean fáciles de mover y los protegen de daños..
• A menudo trabajan con cajas o bolsas., mantener los artículos estables y listos para el transporte.
Máquinas de embalaje
• Centrados en la conservación y presentación de productos individuales.. ellos llenan, sello, y etiquetar artículos para mantener la frescura y la apariencia..
• Garantizar que los productos estén listos para la venta minorista y la exhibición en el mercado., no solo para almacenamiento.
2. Posición en la línea de producción
Máquinas de embalaje
• Ubicado al final de la línea de producción. Operan después de que se hayan completado todos los pasos de empaque primario y secundario..
• Organizar los productos ya empaquetados para su almacenamiento., paletizar, o envío.
Máquinas de embalaje
• Posicionado más cerca del proceso de fabricación. Manejan productos semiacabados y los convierten en envases listos para la venta..
• Sellar bolsas, llenar botellas, o envolver cajas pequeñas antes de la etapa de embalaje.
3. Diferencias técnicas
Máquinas de embalaje
• Centrado en contar, clasificación, y agrupar productos antes del embalaje o embolsado final. Por ejemplo, pueden contar artículos automáticamente, organizarlos ordenadamente, y alimentarlos en contenedores.
• A menudo cuentan con encartonado automático, harpillera, y sistemas de sellado que mejoran la velocidad y consistencia del empaque, especialmente para productos como snacks, piezas pequeñas, o botellas.
Máquinas de embalaje
• Ofrecer un enfoque tecnológico más integrado. Pueden combinar pesaje, relleno, caza de focas, etiquetado, y módulos de inspección en una sola línea.
• Diseñado para vincularse con otros sistemas de automatización como líneas de llenado o etiquetado, permitiendo un flujo de trabajo continuo y optimizado.
4. Materiales y Manejo
Máquinas de embalaje
• Manejar materiales de envío como cajas de cartón., película retráctil, y correas de plastico. Estos materiales se centran en la resistencia y la estabilidad durante el transporte..
• Mantenga grandes volúmenes seguros, apilados correctamente, y fácil de mover.
Máquinas de embalaje
• Manejar materiales en contacto con el producto, como películas., láminas, bolsas, y cajas impresas. Se centran en la calidad y apariencia del sellado..
• Garantizar que los productos se mantengan frescos, limpio, y visualmente atractivo para los consumidores.
5. Salida y velocidad
Máquinas de embalaje
• Diseñado para manipulación a granel. Normalmente procesan 20 a 30 cajas por minuto, dependiendo de la automatización.
• Centrarse en la estabilidad y la carga precisa en lugar de la velocidad máxima de la unidad.
Máquinas de embalaje
• Diseñado para producción a nivel de unidad. Algunas máquinas pueden llenar o sellar más de 100 Paquetes por minuto.
• La velocidad y la precisión afectan directamente la eficiencia, uso de materiales, y calidad del producto.
6. Impacto empresarial
Máquinas de embalaje
• Reducir los costos laborales, evitar daños al producto, y mejorar la eficiencia logística.
• Admitir pedidos de gran volumen y envíos de larga distancia, manteniendo el suministro constante.
Máquinas de embalaje
• Influir en la percepción de la marca a través del sellado de calidad., etiquetado, y presentación.
• Mejorar la confianza del consumidor, cumplimiento minorista, y reputación de marca a largo plazo.
Tabla resumen: Máquinas de embalaje versus máquinas de embalaje
| Aspecto | Máquinas de embalaje | Máquinas de embalaje |
| Función principal | Agrupamiento, caza de focas, preparándose para el envío | Conservación, presentación, embalaje listo para la venta al por menor |
| Etapa de producción | Fin de linea, después del embalaje primario y secundario | Más cerca de la producción, transforma productos semiacabados |
| Tecnología | Cálculo, clasificación, estuchado automático, harpillera, caza de focas | Módulos integrados: peso, relleno, caza de focas, etiquetado, inspección |
| Materiales | Cartulina, película retráctil, correas, cajas | Películas, láminas, bolsas, cajas impresas |
| Producción & Velocidad | Manipulación a granel, 20–30 cajas por minuto, centrarse en la estabilidad | Nivel de unidad, 80–120 unidades por minuto, centrarse en la precisión |
| Enfocar | Logística, protección del producto durante el tránsito | Preparación del mercado, frescura, apariencia, percepción de marca |
| Interacción del consumidor | Indirecto | Directo |
| Impacto empresarial | Reducción de mano de obra, prevención de daños, eficiencia de envío | Mejora de la marca, cumplimiento minorista, confianza del consumidor |
Tipos y aplicaciones de máquinas empacadoras y envasadoras

Tipos comunes de máquinas empacadoras
Máquina empacadora de arcilla/plastilina
• Definición: Una máquina diseñada para manipular materiales blandos., productos maleables como la arcilla, arcilla de moldear, o sustancias similares.
• Características: Llena automáticamente bolsas o contenedores prefabricados con materiales blandos, asegurando uniformidad y mínimo desperdicio.
• Aplicaciones: Ideal para empacar arcilla, arcilla de moldear, compuestos de modelado, y otros productos textiles similares.
Máquina estuchadora
• Definición: Una máquina que forma, cargas, y sella cartones o cajas, Diseñado para embalaje a granel de alta velocidad..
• Características: Tamaños de cartón ajustables, plegado automático, y mecanismos de sellado, a menudo integrado con sistemas de etiquetado.
• Aplicaciones: Utilizado para envasar bebidas embotelladas., bocadillos, productos cosméticos, y otros productos listos para la venta al por menor en cajas de cartón.
Empacadores de casos
• Definición: Máquinas diseñadas para cargar productos automáticamente en embalajes exteriores., cajas o cajas típicamente corrugadas.
• Características: Maneja varios tamaños y configuraciones de productos con sistemas precisos de conteo y alineación..
• Aplicaciones: Ideal para envasar productos enlatados., productos embotellados, piezas pequeñas, o artículos a granel en cajas para su transporte.
Máquinas ensacadoras
• Definición: Máquinas que llenan automáticamente bolsas prefabricadas con variedad de productos, desde artículos granulados hasta líquidos o polvos a granel.
• Características: Sistemas de llenado ajustables y sellado integrado para garantizar un peso constante de la bolsa y sellos seguros.
• Aplicaciones: Utilizado para envasar granos., bocadillos, golosinas, fertilizantes, alimentos para mascotas, y otros productos a granel en bolsas.
Tipos comunes de máquinas de embalaje
Máquina empacadora de flujo horizontal
• Definición: Una máquina que envuelve productos en un movimiento horizontal continuo., formando paquetes sellados.
• Características: Maneja productos de varias formas y tamaños., integra la alimentación, caza de focas, y cortando en una línea.
• Aplicaciones: Adecuado para envasar galletas, golosinas, barras de chocolate, y productos sólidos similares.
Máquina de formado, llenado y sellado vertical (Máquina VFFS)
• Definición: Una máquina que forma bolsas a partir de un rollo de película., los llena de producto, y los sella verticalmente.
• Características: Soporta polvos, gránulos, y pequeños objetos sólidos; formación automática de bolsas, relleno, y sellado.
• Aplicaciones: Ideal para envasar arroz., azúcar, café, bocadillos, y pequeñas piezas de hardware.
Máquina envasadora de film transparente
• Definición: Una máquina que envuelve productos con film transparente estirable para asegurarlos y protegerlos.
• Características: Proporciona una envoltura apretada, Reduce el movimiento de productos., y puede manejar formas irregulares.
• Aplicaciones: Adecuado para bandejas de alimentos frescos., producir, artículos de panadería, y productos en caja.
Máquina de envasado termoformado
• Definición: Una máquina que calienta una lámina de plástico para formar una cavidad., lo llena de producto, y lo sella con una película superior.
• Características: Conformación y sellado de alta precisión, adecuado para embalajes rígidos o semirrígidos.
• Aplicaciones: Comúnmente utilizado para carne fresca., comidas listas para comer, productos lácteos, y blisters.
Cómo elegir la máquina adecuada para su negocio
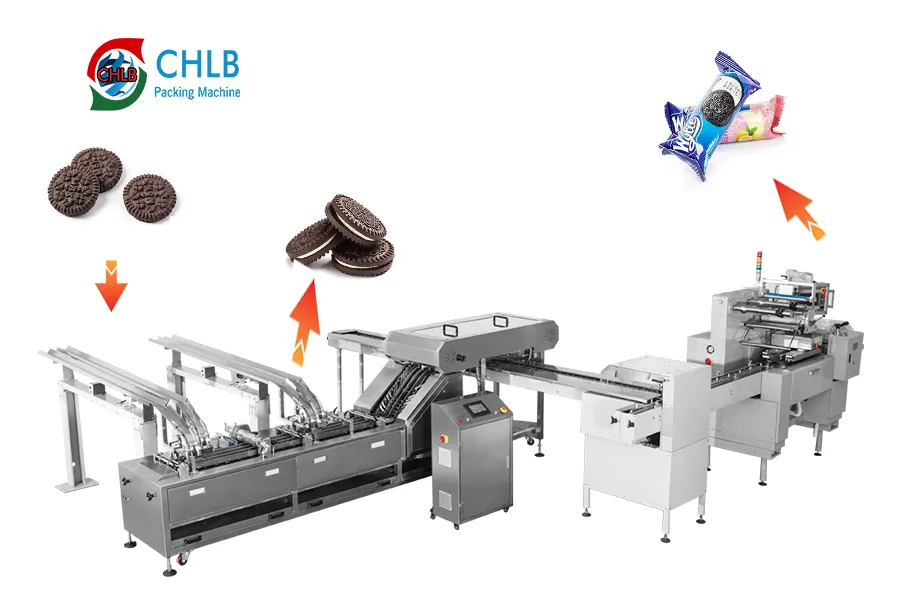
Defina sus requisitos de producto y embalaje
Comience por identificar lo que su producto realmente necesita: embalaje primario (para sellar y proteger artículos individuales) o embalaje secundario (para agrupación y envío).
- Máquinas de embalaje, como envolvedoras de flujo horizontal o sellador de llenado y llenado vertical (VFFS) sistemas, son ideales para manipular productos individuales como snacks, café, o líquidos que necesitan un sellado hermético o una presentación estética.
- Máquinas empacadoras, por otro lado, son mejores para en caja, ensacado, o productos a granel que ya están empaquetados y necesitan ser agrupados o paletizados para su transporte.
La forma de tu producto, fragilidad, y la textura también influyen en la selección de la máquina. Por ejemplo, Las galletas o los jabones encajan bien con las máquinas de envasado continuo., mientras que el arroz o los gránulos son más adecuados para los sistemas VFFS.
Evaluar la capacidad de producción y el nivel de automatización
La escala de producción es uno de los indicadores más sólidos de qué tipo de máquina necesita.
- Para líneas de fabricación de alta velocidad, un sistema de embalaje automático, como una máquina termoformadora o envasadora fluida, Garantiza un funcionamiento continuo y estable..
- Para operaciones de almacén o distribución., Las líneas de envasado semiautomáticas pueden ser más rentables y flexibles..
Los equipos de envasado industrial modernos pueden integrarse con el pesaje, etiquetado, y sistemas de codificación, permitiendo una automatización de línea completa que minimiza la mano de obra y mantiene una producción constante.
Verifique la compatibilidad del material
La elección del material también define el tipo de máquina requerida..
- Máquinas de embalaje manejar películas como PE, MASCOTA, o laminados multicapa utilizados para sellar, pasar la aspiradora, o marca.
- Máquinas empacadoras normalmente se ocupan de materiales para cajas, envolturas encogidas, o películas estirables utilizadas en logística.
Por ejemplo, máquinas de envasado de film transparente requieren una película altamente estirable, mientras máquinas VFFS Necesita películas en rollo adecuadas para termosellado.. Garantizar la compatibilidad adecuada del material garantiza un funcionamiento sin problemas, sellos fuertes, y seguridad del producto.
Revisar mantenimiento, Apoyo, y disponibilidad de repuestos
Ya sea que elija una máquina empacadora o empacadora, Un servicio postventa confiable es esencial.. Busque proveedores que ofrezcan capacitación para operadores, asistencia tecnica, y entrega rápida de repuestos. Componentes de alta calidad, como sensores de marca, Sistemas PLC, o módulos eléctricos, mejorar la estabilidad de la máquina y simplificar el mantenimiento a largo plazo.
Evaluar el presupuesto y el retorno de la inversión
Tu decisión debe ir más allá del coste inicial. Una máquina de bajo precio puede resultar en más tiempo de inactividad o mayor desperdicio de material, mientras que un sistema automático premium podría ofrecer un retorno de la inversión más rápido a través de una mayor eficiencia y precisión.
Al comparar opciones, calcule su costo total de propiedad, incluyendo mantenimiento, mano de obra, y consumo de energía. Para empresas en expansión, elija un sistema que permita futuras actualizaciones o personalización para escalar con su crecimiento.
Pensamientos finales
Las máquinas empacadoras y las máquinas empacadoras desempeñan cada una un papel único en la cadena de producción., desde proteger artículos individuales hasta preparar productos terminados para su envío. Cuando combinas la máquina con el producto, los materiales, y sus objetivos de producción, no sólo reduce el desperdicio y la mano de obra, sino que también crea un ambiente más fluido., operación más confiable.
Si todavía está decidiendo qué solución se adapta mejor a su negocio, CHLB está aquí para ayudar. Con años de experiencia en automatización industrial y sistemas de embalaje y embalaje personalizados., CHLB le apoya desde la evaluación inicial del proyecto hasta la instalación, capacitación, y mantenimiento a largo plazo. No es necesario que resuelvas todo solo., y lo guiaremos a través de cada detalle para asegurarnos de que invierta con confianza..
Listo para mejorar la eficiencia y optimizar su línea de producción?
Comuníquese con CHLB, y encontremos las máquinas que realmente funcionan para su negocio.
Preguntas frecuentes
1. ¿Cómo funciona un Trabajo de la máquina de envasado termoformado.?
Calienta y da forma a la película plástica en bandejas o cavidades personalizadas., luego llena y sella el producto. Esto crea fuertes, Envases herméticos comúnmente utilizados para alimentos y artículos médicos..
2. ¿Cuáles son los diferentes tipos de máquinas de envasado de flujo?
Los dos tipos principales son las envolvedoras de flujo horizontal y las envolvedoras de flujo vertical.. Los modelos horizontales se adaptan a artículos sólidos., mientras que los modelos verticales manejan polvos o productos granulados.
3. Qué es una máquina empacadora de arcilla?
pesa, llena, y empaqueta bloques de arcilla o plastilina en bolsas o envoltorios. La máquina asegura un peso constante y apretado., embalaje limpio.
4. ¿Cómo se utiliza un máquina de embalaje de plastilina?
Ajuste las configuraciones de peso y velocidad según su producto, y la máquina automáticamente porciona y envuelve la arcilla. Mantiene el embalaje uniforme y limpio..
5. ¿Qué es una máquina envasadora??
Maquinaria de embalaje Se utiliza en todas las operaciones de embalaje., involucrando paquetes primarios a paquetes de distribución. Esto incluye muchos procesos de embalaje.: fabricación, limpieza, relleno, caza de focas, combinatorio, etiquetado, envoltura, y paletizado.















